Anatomy : -There are 2 kidneys , they are bean shaped and reddish brown.- They are located between the peritoneum and the posterior wall of the abdomen.- Dimensions : 4 x 2 x 1 inches_____
Layers :
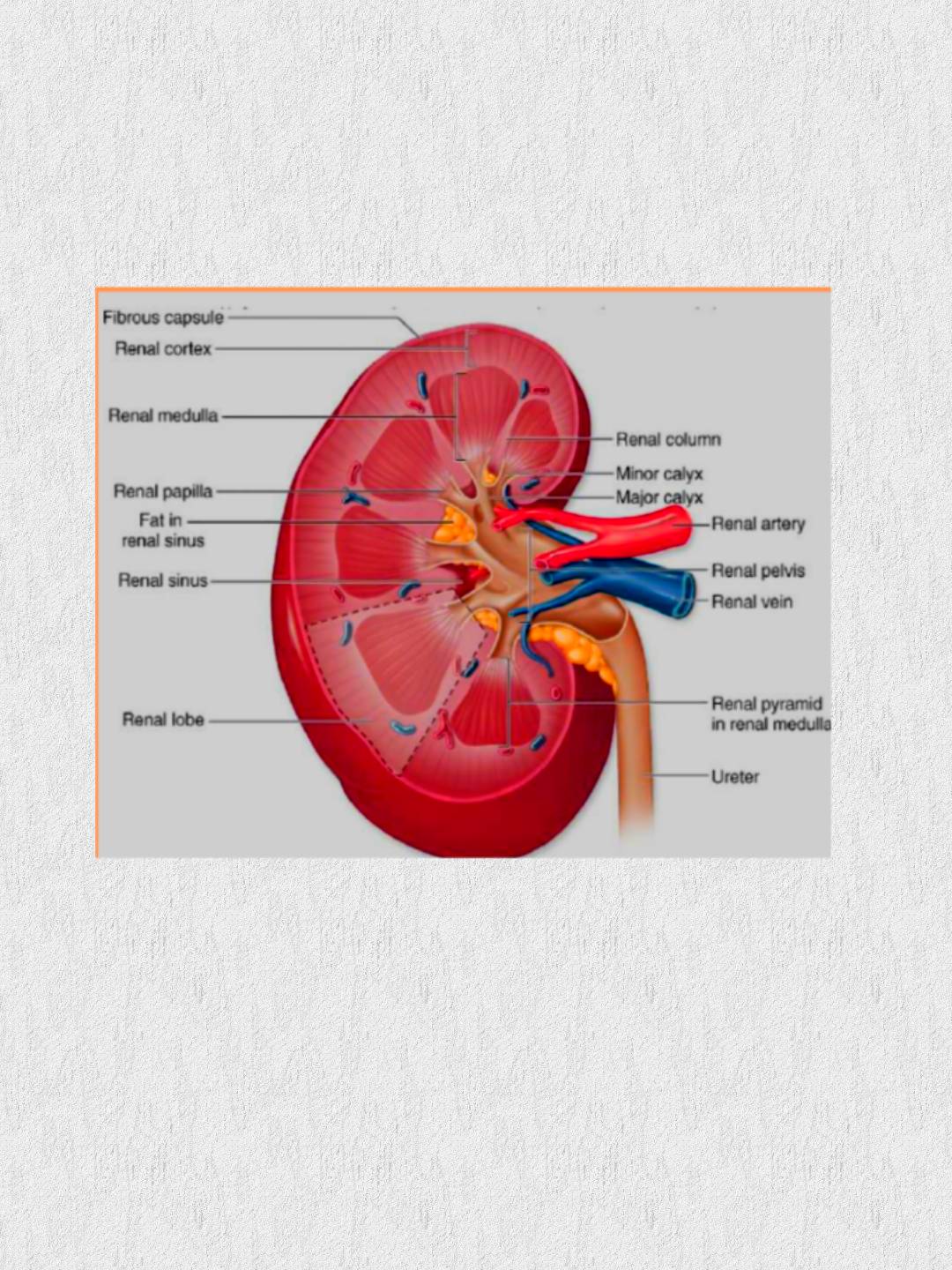
Cortex: superficial layer.Medulla
: Inner portion , arranged in pyramids , there are 8 – 18 pyramids per
addicted to it
kidney separated by renal columns. The apex of each pyramid extends toward
the renal pelvis and forms a papilla which projects into minor calyces → major
the renal pelvis and forms a papilla which projects into minor calyces → major
calyces, which in turn unite to form renal pelvis.
The nephron : the functional unit of the kidneyThere are approximately one million nephrons in each kidney.
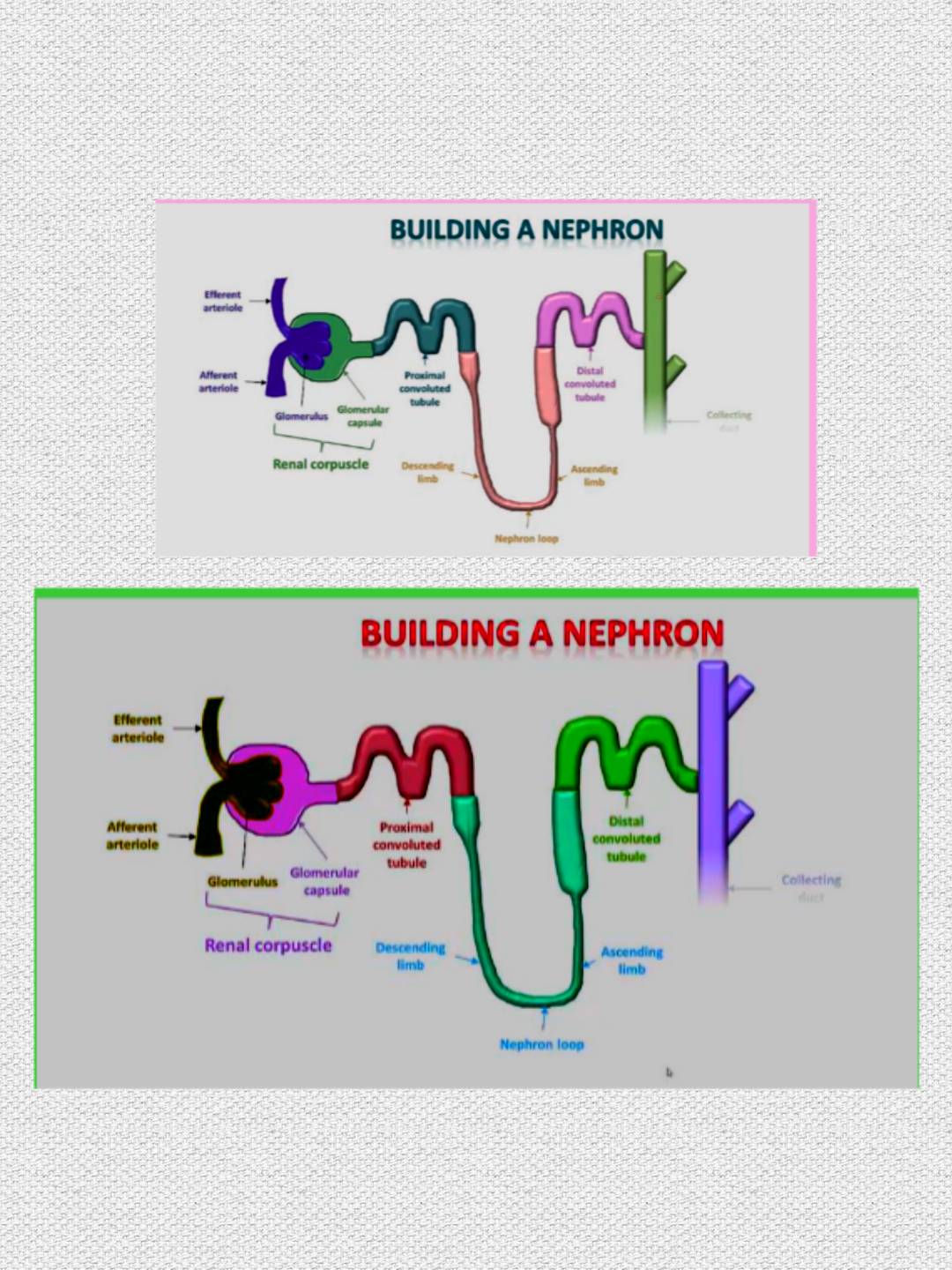
Renal corpuscle : Bowman’s capsule & the glomerulus within it : It is the site offiltration of the blood.
2. Proximal convoluted tubule
.3. Loop of henle.
4. Distal convoluted tubule
.5. Collecting duct : drains into the renal pelvis.
Renal blood flow :- The kidneys get 20 – 25 % of cardiac output.- Renal artery divides to form interlobar arteries ( that run between the medullarypyramids ) → arcuate arteries (run in the corticomedullary junction) → interlobulararterioles ( run in the cortex ) → Afferent arterioles → Glomeruli → Efferentarterioles which divide into the vasa recta and the peritubular capillaries , this is anetwork of capillaries which allows movement of fluids and solutes out of thetubules.Functions :Regulation of water & electrolyte balance. Regulation of acid base balance
Regulation of acid base balance.
Excretion of water soluble waste : urea , uric acid , creatinine , drugs ……
Endocrine : Renin – angiotensin system , erythropoietin , vitamin D activation.
Glomerular filtration rate : It is the volume of fluid filtered from the renal glomerular capillaries intoBowman’s capsule per minute.In an average man : GFR = 125 ml/min. In women : 10% less than those of men.Clinically , GFR is often measured to determine the renal function.Although the GFR is about 180 L / day , our urine output is only 1-2 L/day (which is good or else we’d spend the day in the bathroom
Investigation Of Renal DiseasesAima) To prove the condition.b) To asses the severity.c) Investigation for the cause.
Urinalysis : physical , chemical , microscopic ( details : see later )
Urine culture & sensitivity : for UTI
2- Blood investigations : K : 3.5 – 5 mEq/Lo CBC. Na , K , Ca , P
.o Urea , Creatinine , PH
Renal function test :For glomerular function : Measurement of :

Renal function test :For glomerular function : Measurement of :i. Serum Creatinine ( N : 0.7 – 1.4 ) :it’s produced from muscle cells at a constant rate , so its plasmaconcentration depends on its excretion, which reflects GFR.Small change in creatinine are associated with large change in GFR,and so plasma creatinine is an insensitive marker of early renal
disease.
. Blood urea ( N : 20 – 40 mg% ) :Less reliable as it is affected by dietary protein & liver failure.
iii. Creatinine clearance :Volume of plasma which is cleared from creatinine in one minute.

Others ___Inulin clearance : inulin is a small molecule, freely filtered by the glomeruli& with no tubular secretion.Chromium-labelled EDTA.For tubular function :Specific gravity & urine osmolality.Urine concentration test.Urine dilution test .Renal imaging :i.
Plain X-ray of urinary tract.ii. Renal ultrasound : it demonstratesa) Bipolar renal length ( 8.5 – 13.5 cm ) :In CRF : the kidneys are small. The exceptions are
: MCQPolycystic kidney disease :
large with multiple cysts.Diabetic nephropathy , Amyloidosis : normal size.In ARF : the kidneys are normal size , enlargement may occur due toswelling
. b) Doppler ultrasound is useful to assess renal blood flow.c) Renal stones, mass lesions , cysts.iii. Intravenous urography ( IVU ) & ascending pyelography.iv. CT , MRI .


